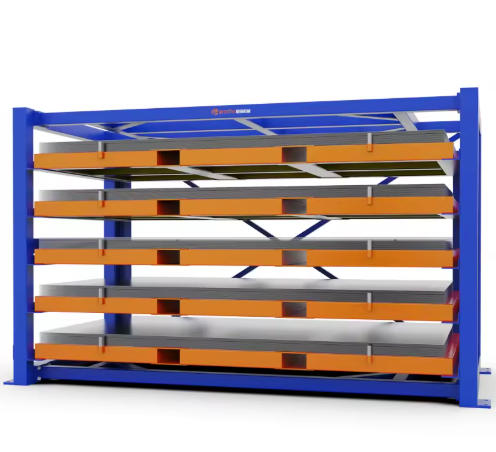
Heavy-Duty Pull-Out Sheet Drawer Racks
Industrial storage equipment must match specific operational parameters—generic solutions create inefficiencies and safety hazards. Heavy-duty pull-out sheet drawer racks address this through modular engineering that adapts to material weights, dimensions, and facility constraints. Understanding the technical specifications enables informed procurement decisions.
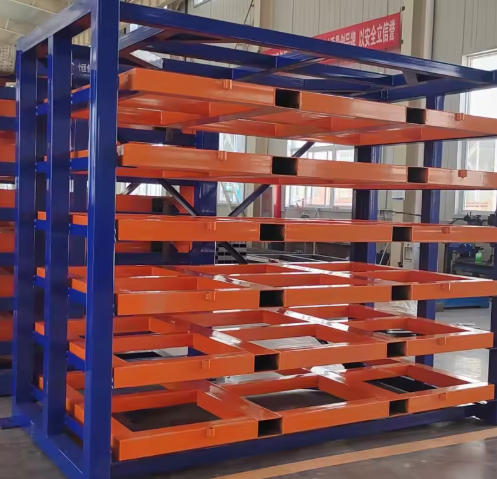
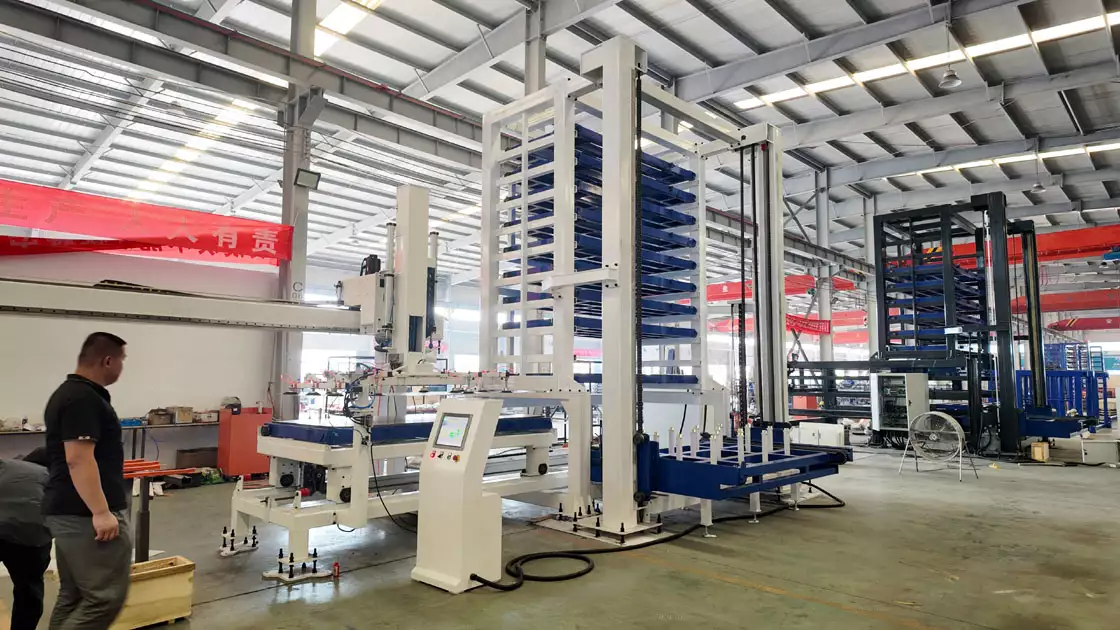
The 20-ton per layer capacity represents structural engineering across multiple components. Frame uprights use high-tensile steel columns, typically 100×100×5mm box sections, welded to horizontal beams forming the support grid. This base structure distributes concentrated loads across the floor footprint, reducing point loading stress.
Heavy-Duty Pull-Out Sheet Drawer Racks: Engineering Analysis of Load Capacity and Customization Systems
Industrial storage equipment must match specific operational parameters—generic solutions create inefficiencies and safety hazards. Heavy-duty pull-out sheet drawer racks address this through modular engineering that adapts to material weights, dimensions, and facility constraints. Understanding the technical specifications enables informed procurement decisions.
Load Bearing Mechanics
The 20-ton per layer capacity represents structural engineering across multiple components. Frame uprights use high-tensile steel columns, typically 100×100×5mm box sections, welded to horizontal beams forming the support grid. This base structure distributes concentrated loads across the floor footprint, reducing point loading stress.
Guide rails undergo specialized heat treatment. Standard rails handle 3-5 ton loads through induction-hardened steel tracks. For 8-10 ton applications, rails incorporate recirculating ball bearing systems with sealed lubrication chambers. The 20-ton ultra-heavy configuration uses dual-rail systems—two parallel tracks per drawer—effectively halving the load per rail while doubling stability.
Drawer construction varies by capacity. Light-duty units (3-5 tons) use formed steel pans with cross-bracing. Heavy-duty models (8-10 tons) employ welded steel frameworks with reinforced decking. Load distribution panels prevent point loading from material bundles, ensuring even weight transfer to rails.
Dimensional Engineering Standards
Standard models follow precise dimensional protocols. The 3505×2280×2000mm overall size for HC-B3015-63 breaks down as follows: 3505mm length accommodates 3000mm sheets plus 500mm operating clearance; 2280mm depth handles 1500mm sheet width plus 780mm for the slide mechanism and safety spacing; 2000mm height positions six layers at ergonomic access levels.
Width customization expands the 2280mm depth dimension proportionally. A facility storing 2000mm wide sheets would specify 2880mm depth—maintaining the 880mm mechanism allowance. Height customization considers ceiling clearance and material handling equipment reach. Maximum practical height typically reaches 4000mm for manual access, 6000mm when used exclusively with overhead cranes.
Layer Customization Mathematics
Layer count derives from material thickness and required storage capacity. The calculation follows: (Total Height – Base Clearance – Top Clearance) / (Material Thickness + Drawer Mechanism Thickness). For 2000mm overall height storing 25mm panels: (2000mm – 150mm base – 150mm top) / (25mm + 35mm mechanism) = 1700mm / 60mm = 28 potential layers. Practical limits reduce this to 6-8 layers based on weight distribution and access frequency.
The customization process evaluates material mix. A metal shop storing 2mm, 5mm, and 10mm steel sheets in equal proportions receives three drawer sizes optimized for each thickness. This prevents wasted vertical space that occurs with uniform layer spacing.
Safety System Engineering
Maximum load signs position at eye level on each upright, visible from normal operating distance. These aren’t simple stickers—they’re embossed metal plates with permanent markings, preventing wear or removal. Signs indicate both static load capacity and dynamic load limits during drawer operation.
Anti-pinch design incorporates multiple approaches. Primary protection comes from 50mm gaps between drawer sides and frame members. Secondary protection uses recessed handle designs that place hands away from closing edges. Tertiary systems employ pressure-sensitive edges that stop drawer motion if obstruction detection occurs during powered operation.
The label system’s transparent sleeves fit into extruded aluminum channels riveted to drawer fronts. Standard card dimensions are 100×150mm, visible from 5 meters. Some installations integrate QR codes linking to digital inventory systems, enabling real-time stock verification via mobile devices.
Integration with Lifting Systems
Gantry crane compatibility requires precise drawer extension characteristics. The drawer must extend fully (typically 90% of length) while supporting rated load at full extension. Rail systems include locking mechanisms at 50%, 75%, and 100% extension points, allowing precise positioning for crane loading.
Crane operators lower plates onto extended drawers using standard slings or vacuum lifters. The drawer surface includes polyurethane strips preventing metal-on-metal contact that causes scratches. Once loaded, operators release the extension lock, and the drawer retracts smoothly.
Ladder truck integration focuses on stability. Platform trucks lock to the rack frame using adjustable clamps engaging the upright columns. Platform height adjusts in 100mm increments via pin locks, aligning with drawer levels from 800mm to 3000mm. Guardrails surround three sides, with the fourth side open for drawer access.
Installation and Foundation Requirements
Floor preparation varies by model. The HC-B3015-63 exerts approximately 0.5 tons per square meter when fully loaded—manageable for most industrial floors. The HC-B6020-610 concentrates 3.8 tons per square meter, requiring reinforced concrete pads or steel foundation plates distributing load across wider areas.
Anchoring systems use expansion bolts for concrete floors or chemical anchors for epoxy-coated surfaces. Bolt patterns match the frame base dimensions, typically eight bolts per upright. Installation tolerances allow ±5mm vertical adjustment through leveling bolts compensating for floor irregularities.
Maintenance Protocols
Quarterly maintenance includes rail lubrication using lithium-complex grease rated for high-pressure applications. Inspect roller bearings for wear patterns indicating misalignment. Check drawer stops and locking mechanisms for proper engagement. Annual procedures involve ultrasonic testing of welded joints and magnaflux inspection of critical stress points.
Predictive maintenance uses acoustic monitoring for high-throughput installations. Sensors detect vibration pattern changes in rail systems, indicating bearing degradation before failure. This data-driven approach prevents unexpected downtime in facilities operating multiple shifts.
Factory









Hot Selling Machines
-
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Intelligent Production Line CNC Automated Storage Rack: Precision Meets Automation
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Drawer-Style Sliding Sheet Metal Storage Rack – Efficient & Safe Material Handling
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Sliding Drawer Design for Steel Plate Storage with Heavy Duty Drawer Type Sheet Metal Rack Storage System
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Sliding Drawer Rack for Heavy Plates and Molds: Durable, Efficient Storage for Industrial Applications
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Drive-In Pallet Rack Alternative: Space-Saving Drawer-Type Sheet Metal Storage with Automated Retrieval Compatibility
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Heavy-Duty Drawer Type Plate Shelves Warehouse Rack System for Industrial Metal Storage – 3-Ton Capacity per Layer
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Heavy-Duty Warehouse Storage System: Customizable Solutions for Metal Plate & Industrial Storage
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Automated Storage Systems
Smart Fixed Profile Stereo Warehouse: Cost-Effective Automation for Small to Mid-Sized Fabrication Shops
Read moreRated 0 out of 5
Related products
Related products
-
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Heavy Duty Forklift aluminum plates storage equipment
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Heavy Duty Shelves Built for Sheet Metal—Not Afterthoughts
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Heavy Duty Sheet Metal Storage Racks
Heavy Duty Flat Products Storage Racks
Read moreRated 0 out of 5